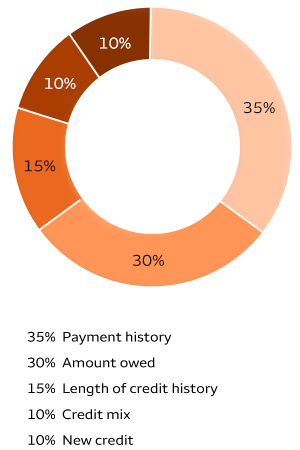
The time series evolution of credit scores provides a great way to see the effects of removing or adding certain credit characteristics. These attributes can make a big difference in a person’s credit score. The article also addresses the effects of dropping credit characteristics and the effects high-cost credits have on credit scores.
Credit scores over time
In many credit decisioning models, time series data is an important component. This data is used by lenders to determine the risk of a customer's credit history. It tracks how a consumer pays bills over time. Lenders may be able to see more detail about borrowers' past history of late payments by using time series data from credit card balances.
This data is generally positive but can show a downward trend. This is especially true for consumers in lower risk and lower scoring segments. Recent declines in hard credit inquiries could be due to a renewed consumer focus on reducing spending, and paying down their debt.

The impact of dropping credit characteristics related to groups
One study looked at how removing a set of credit characteristics could affect a credit score. The average credit score was able to be lowered by 2.5 points or approximately one-fifth. People with lower credit scores had greater changes than those with higher credit scores.
Dropping a single characteristic from a credit score had very little effect on the mean score for blacks. The average change in black credit scores was 0.1 points. This small change can be attributed to the high correlation between these characteristics and the scoring model. These differences held across the three scorecards.
Effects of adding other characteristics
Traditional credit score analysis has focused on the effects of one characteristic such as age. Although the effects of adding another characteristic aren't well understood, an additional characteristic may have a significant impact. To determine the effects of adding another characteristic to the model, each scorecard model was re-estimated and compared with the FRB base model.
Although it did not affect the mean score, including race or ethnicity would have an effect on its predictive value. However, removing these attributes would cause a significant decrease of model predictiveness for others.
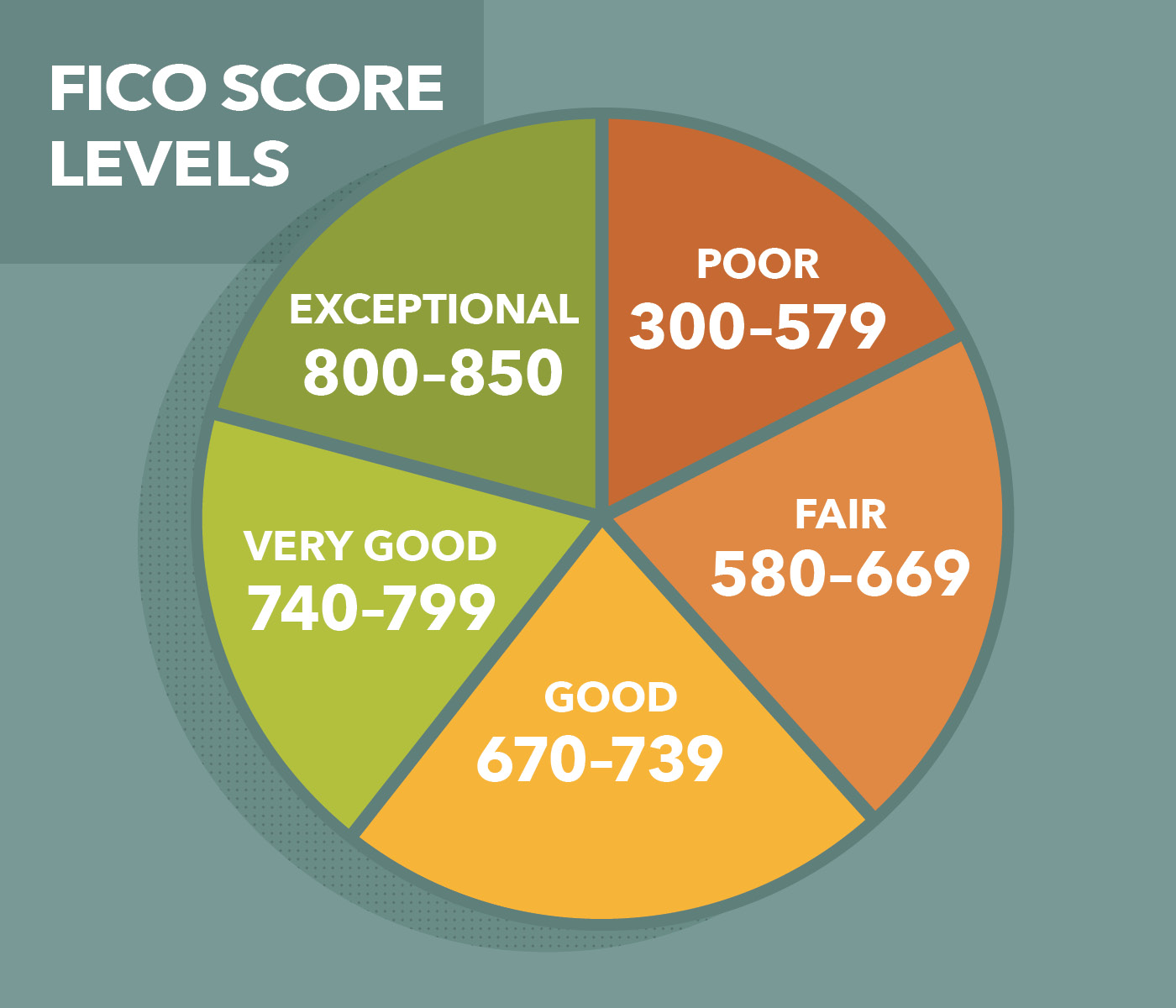
High-cost credit: The effects
High-cost debt can have a negative impact on credit scores for a number of reasons. It signals lenders that the borrower is a high-risk credit risk. Second, high-cost loans can result in higher defaults. These defaults can have adverse effects on the overall financial position. Third, high-cost credit has a negative effect on the social reputation of the borrower.
High-cost credit may reduce the demand for traditional sources of financing and could limit future access. High-cost credit can also lead to borrowers choosing high-cost credit as a more risky option. This may be a good option for short-term financial problems, but it can also limit the availability of traditional sources of financing.